Introduction
In an age where technology drives innovation, cloud computing has emerged as the backbone of the business. Among the cloud providers, AWS stands out for its services, versatility, reliability. Whether you are an entrepreneur, working professional understanding AWS can transform how to build and manage the application. In this blog we will explore what AWS is, its features, its services, its global infrastructure and how to get started.
What is AWS?
AWS refers to Amazon Web Services, which is a cloud services platform that provides services via the internet. Users can host applications, store data, and run other activities without having to manage physical servers and data centers.
AWS was launched in 2006. Today, it offers scalable, cost effective, and secure solutions to individuals, from startups to large enterprises. AWS functions on a subscription model which means you pay only for the services you use.

Key Features of AWS
- Services: AWS lists more than 200 services that include computing, storage, database, networking, analytics, and more.
- Scalability: Enables users to scale the resources up or down depending on the need. Performance and cost-efficiency are ensured.
- Global Availability: Operates within 31 geographic regions in 99 Availability Zones ensuring high availability and low latency anywhere in the world.
- Security: Offers a security framework with encryption, access control, and compliance certification including ISO and GDPR.
- Cost-Effective: Eliminating the need for upfront infrastructure investments through the pay-as-you-go pricing model ensures AWS is accessible to all organizations.
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS global infrastructure is one of the important features, ensuring reliable and faster delivery worldwide.

Key Components of AWS Global Infrastructure
Regions: A region is a physical location across the globe where the AWS has data centers. Each region has multiple availability zones. AWS currently operates in 31 geographic regions.
Availability Zones : Availability zones are fully isolated locations within a region. They are connected through low-latency, high-speed fiber, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. AWS currently has 99 Availability Zones globally.
Edge Locations: Edge locations are part of the AWS Content Delivery Network (CDN), known as AWS CloudFront. These ensure that content is delivered with minimal latency to users worldwide.
Local Zones: Local Zones bring AWS services closer to users, offering ultra-low latency for applications requiring proximity to end users.

Services provided by AWS
Compute Service
AWS Lambda : Allows running of code based on specific events without necessitating the use of dedicated servers.
Amazon EC2: Offers virtual computers to deploy the applications in the form of scalable servers.
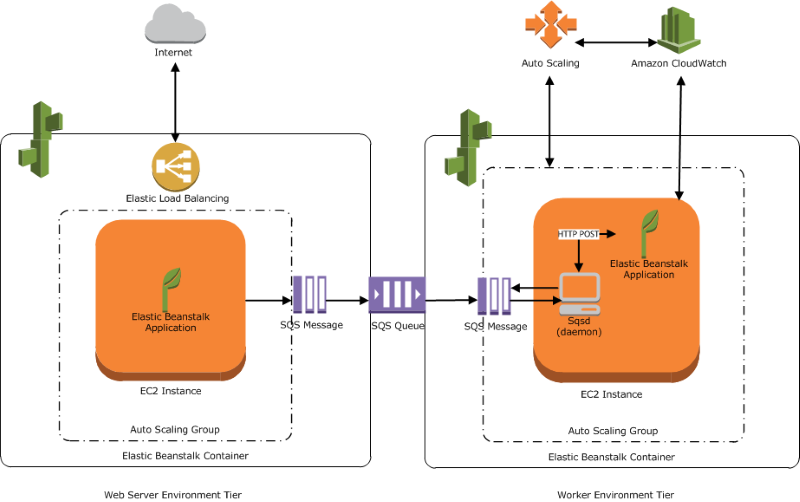
Elastic Beanstalk: Offers streamlined management as well as smoothing the deployment of newer applications.
Storage Services
Amazon EBS: Block level data storage that can be used with EC2 instances is provided by this service.
Amazon S3: An object storage service is offered for storing files, backups, and even big datasets that grow with use.
Amazon Glacier: Cost effective storage for long-term retention as well as keeping archived data for years.
Database Services
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Managed My SQL and postgreSQL databases are offered by AWS.
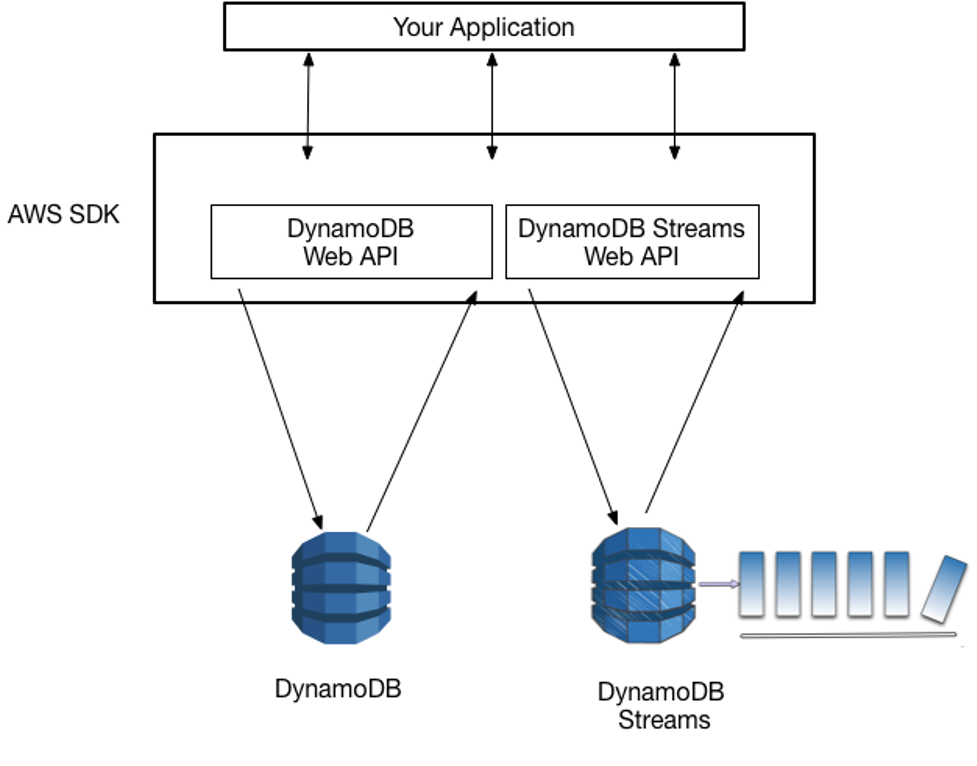
DynamoDB: a NoSQL database that serves swift and highly scalable applications.
Amazon Redshift: Known to be data warehouses that serve the purpose of analytics and reporting.
Networking and Content Delivery
Virtual Private Cloud: It offers clusters that are private and reserved for certain patrons that provide advanced security to the services.
Amazon CloudFront: CDN associate that delivers content from all corners of the world without geographic restrictions.
Route 53: Serves to manage Domain Name Systems the same way as at scale.
Machine Learning and AI
Amazon SageMaker: Specialized in the creation of algorithms and preparing, training them into use
Amazon Rekognition: Handles the image and videos and serves the purpose of analysing them.
Developer Tools
AWS CodePipeline: Automates software release workflows.
AWS CloudFormation: Infrastructure-as-code for managing AWS resources.
AWS CodeBuild: A fully managed build service for CI/CD.
Monitoring and Management
Amazon CloudWatch: Observes system performance, along with metrics and logs.
AWS Config: Observes resource configuration settings and manages them.
AWS Trusted Advisor: Provides recommendations for cost efficiency, security, and balance monitoring.
How to get started with AWS
Step 1: Set Up an AWS Account
Go to the AWS page and register for an account. New users are offered a Free Tier to test and interact with its services under specific usage limits
Step 2: Explore the AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console is an interactive web-based platform that allows users to navigate and manage the services. It is advisable to get acquainted with it to understand its structure and functionalities.
Step 3: Start with Basic Services
First, explore core services such as EC2, S3, and RDS. Playing around with these services can help you better understand how AWS functions.
Step 4: Review AWS Guides, Documentation, and Tutorials
AWS offers comprehensive documentation as well as beginner guides, and tutorials. These materials are designed to help you strengthen your understanding.
Step 5: Undertake a Simple Task
Put your learning into practice by creating a static website and hosting it on S3 or deploying a simple app on EC2. Practical exposure is the most effective way to learn.
Step 6: Explore Certification in AWS
A good starting point of exploration is the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certification which will help you document your understanding and knowledge of basic cloud concepts.
Conclusion
AWS has redefined the way we think about infrastructure and computers. The firm holds a commanding lead in cloud computing due to its advanced infrastructure spanning the globe, comprehensive catalogue of services, and unwavering commitment to technological advancement. No matter your expertise, AWS provides the necessary assets and systems to succeed in this fast changing world.
Unlock AWS today to access boundless prospects for innovation, creation, and cloud expansion. For more blogging related to Cloud and DevOps, check out DevOps Horizon.